REDIS SERVE
Redis is an in-memory data structure that is used for faster access to data. It is used to store data that needs to be accessed frequently and fast. It is not used for storing large amounts of data. If you want to store and retrieve large amounts of data you need to use a traditional database such as MongoDB or MYSQL. Redis provides a variety of data structures such as sets, strings, hashes, and lists.
The Redis server is a program that is running and stores data in memory. You can just connect to that server and can use it to store and retrieve data faster. For that reason, Redis is not used for persistent storing of data as complete data will be lost if the system crashes. Redis is scalable as you can run multiple instances of the server. It is often used as a cache that stores data temporarily and provides faster access to frequently used data.
When to use Redis Server?
Consider you have a MySQL database and you are constantly querying the database which reads the data from the secondary storage, computes the result, and returns the result, if the data in the database is not changing much you can just store the results of the query in redis-server and then instead of querying the database which is going to take 100-1000 of milliseconds, you can just check whether the result of the query is already available in redis or not and return it result which is going to be much faster as it is already available in the memory.
In a messaging app, Redis can be used to store the last five messages that the user has sent and received using the built-list data structure provided in Redis.
Advantages of Redis Server
- Speed: Redis stores all the data in memory which allows fast read and write operation making it ideal for applications that need faster access to the data.
- Flexible: Redis provides various types of data structures such as lists, strings, sets, and hash which makes it usable for various types of applications such as caching, session management, etc.
- Scalability: Redis is highly scalable as it can be scaled out by adding more Redis servers.
How to Start Redis Server?
To start the Redis server on your machine you need the run the below command in the terminal:
redis-server
Redis and its role in System Design
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker. It is widely used for its fast performance, flexibility, and ease of use.
|
Redis Data Storage Types
Redis allows developers to store, retrieve, and manipulate data in various data structures such as strings, bitmaps, bitfields, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, geospatial, hyperlogs, and streams.
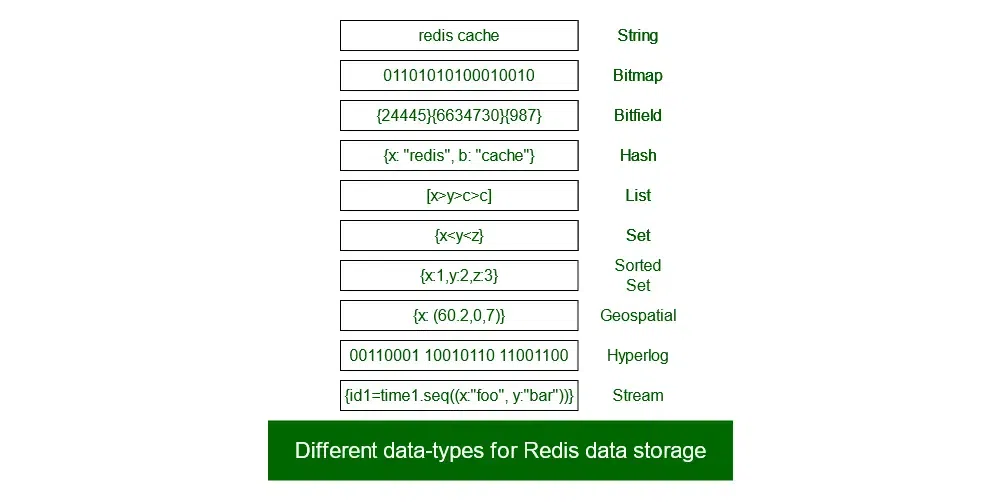
Redis data types
Benefits of using Redis
All Redis data resides in the server’s main memory, in contrast to databases such as PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and others that store most data on disk. Redis can therefore support higher orders of magnitude of operations and faster response times. Thus, it results in super-fast performance with average read and writes operations taking less than milliseconds, and thus accordingly supports millions of operations per second.
Redis provides an overall system that offers us caching systems in both types of architectures – monolithic and distributed, thereby making the retrieval of data faster, as the direct access operation, by key in memory(like hashtables), will reduce the overall complexity of reading the data from the original SQL Database.
How redis is useful for caching
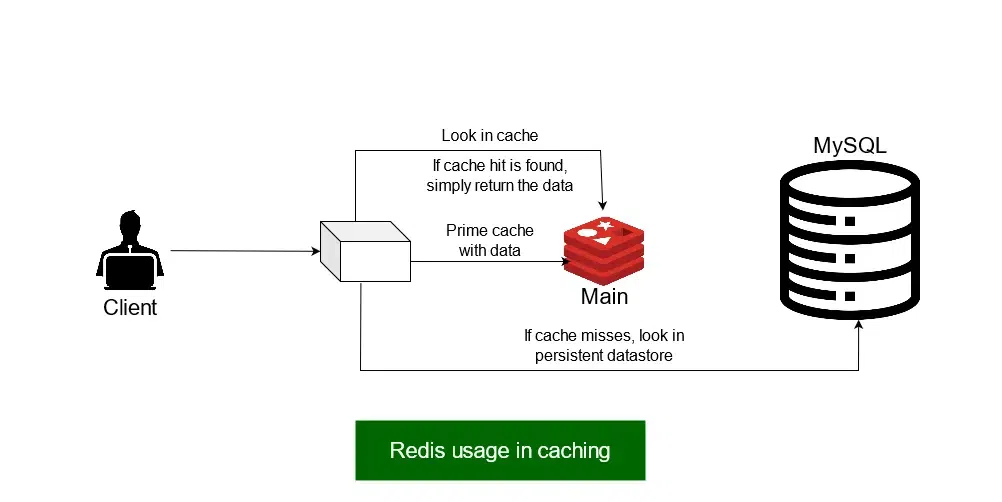
Working Architecture of Redis
There are several Redis architectures, depending on the use case and scale:
1. Single Redis Instance
This is the most straightforward Redis deployment. It involves users setting up and running small instances that can help them grow and speed up their services. However, it has its own drawback, as all calls made to Redis would fail if this running instance crashes or is unavailable. Thus there is a degradation in the overall performance and speed of the system.

Single Redis Instance
2. Redis HA (High Availability)
- Another popular setup is the main deployment with a secondary deployment that is always kept in sync with the replication. The secondary instances can be one or more instances in our deployment, which helps in scale reads from Redis, and provide failover in the case when the main is lost.
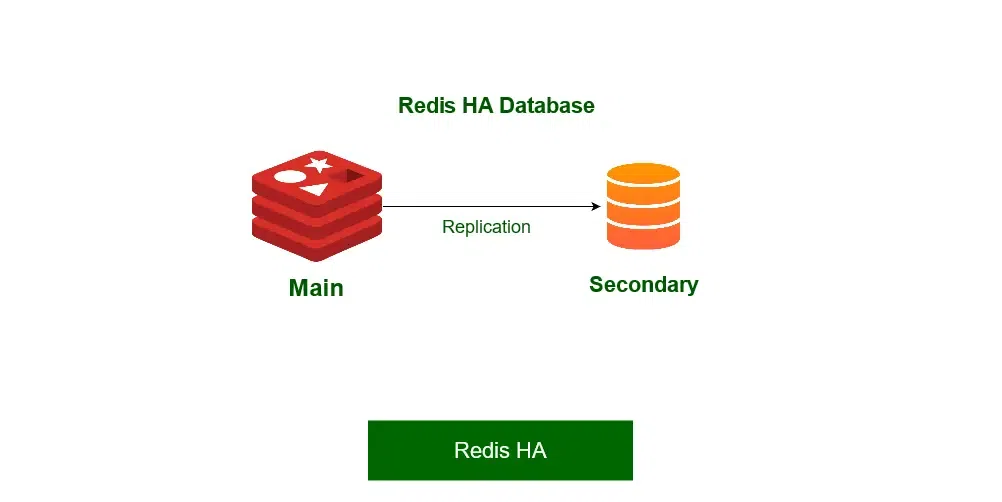
Redis HA (secondary failover)
3. Redis Sentinel
- Sentinel corresponds to a distributed system. It is designed in a way where there is a cluster of sentinel processes working together for coordination of state to provide constant availability of the Redis system. Here are the responsibilities of the sentinel:
- Monitoring: Ensuring main and secondary instances are working as expected.
- Notification: Notify all the system admins about the events occurring in Redis instances.
- Management during failure: Sentinel nodes can start a process during failure if the primary instance is not available for long enough, and enough nodes agree that it is true.
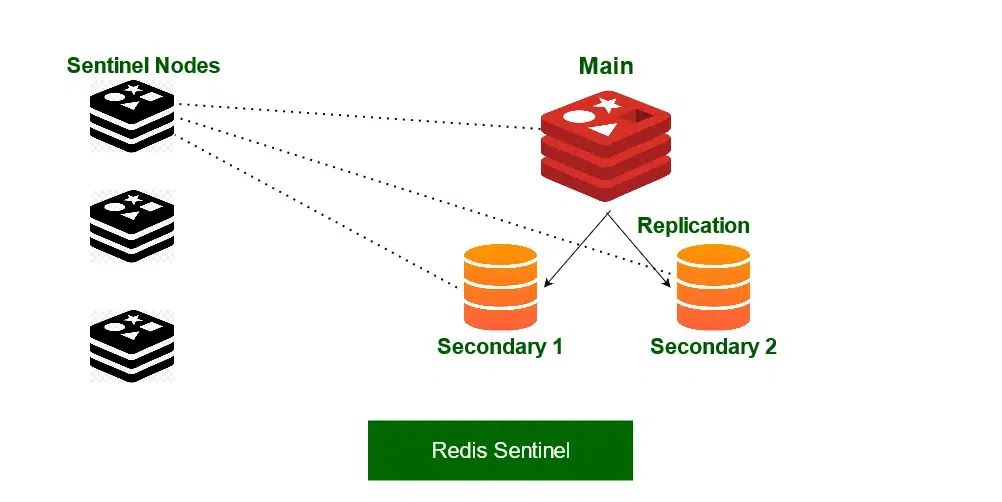
Redis sentinel
4. Redis Cluster / Redis Cluster Master-Slave Model: The Ultimate Architecture of Redis
The Redis cluster is the ultimate architecture of Redis. It allows for horizontal scaling of Redis.
In Redis cluster, we decide to spread the data we are storing across multiple machines, which is known as Sharding. So each such Redis instance in the cluster is considered a shard of the whole data.
The Redis Cluster uses algorithmic sharding. To find the shard for a given key, we hash the key and mod the total result by the number of shards. Then, using a deterministic hash function, meaning that a given key will always map to the same shard, we can reason about where a particular key will be when we read it in the future.
.png)
Redis Cluster Architecture in System Design
To handle further addition of shards into the system (resharding), the Redis cluster uses Hashslot, to which all of the data is mapped. Thus, when we add new shards, we simply move hashslots from shard to shard and simplify the process of adding new primary instances into the cluster. And to the advantage, this is possible without any downtime, and minimal performance hit. Let’s look at an example below:
Consider the number of hashslots to be 10K.
Instance1 contains hashslots from 0 to 5000,
Instance2 contains hashslots from 5001 to 10000.Now, let’s say we need to add another instance, now the distribution of hashslots comes to,
Instance1 contains hashslots from 0 to 3333.
Instance2 contains hashslots from 3334 to 6667.
Instance3 contains hashslots from 6668 to 10000
Comments
Post a Comment